Reporting on Economic Inequality: Tips from Our Newsletter
Last Updated March 2024
The guidance below collects the thoughts, tips, and must-reads about reporting on economic inequality published in our weekly newsletter, Revisions. The information is presented in roughly chronological order, has been edited for clarity, and is updated where necessary.
Language & Word Choice
November 18, 2021
What’s the best way to describe the tight labor market in the U.S.?
Many outlets have been referring to this supply-and-demand problem as a “labor crisis” or “worker shortage,” but these phrases are imprecise. While November 2021 reports said there were more jobs than jobless people in 42 states, we’re also experiencing “The Great Resignation,” during which a record number of Americans are quitting jobs because they are less willing to accept low pay, insecurity, and inflexibility in the workplace. The term “labor shortage” does address a supply-demand gap, but it doesn’t capture why many are leaving the workforce. Labeling the crisis by its roots rather than its result helps audiences understand systemic cause and effect. When describing why people are leaving the workforce, for instance, “living wage shortage” or “benefits crisis” might be more accurate.
January 20, 2022
What’s the difference between “low-wage” and “low-income?”
The phrases “low-wage” and “low-income” are often used interchangeably when referring to workers, but I do believe there is a subtle important difference that journalists and word-nerds should pay attention to. Income refers to what someone receives, implying the recipient has the agency in what they’re receiving. Whoever’s on the other end of this give-and-take is absent in that phrase. (I.e., if your income is low, it’s on you.) A wage, however, refers to what someone is given by their employer; the employer has the agency. (I.e., if your wage is low, it’s on your employer.) So, in discussions about workers and how wages are affecting employment, economic security, and public health, using “low-wage” to focus on what employers are paying workers is likely more appropriate.
August 11, 2022
Economic news moves fast, so following the trajectory of inflation or a potential recession can be tough for audiences. Layer on financial jargon and pretty soon you’ll find readers and viewers tuning out news that they need to thrive. How can journalists help explain it all? Turn to service journalism.
“Service journalism, of course, is a new term for an old idea: giving readers good, practical advice — what to buy, where to go, how to do a certain thing — to make their lives easier. While service journalism shares the same standards of truth and fact-finding as regular reporting, it requires a different approach. The biggest shift: The reporter’s lens moves from the subject to the reader.” — The Reynolds Journalism Institute.
Use the links below as guideposts. Each piece uses a different tactic to make economic news useful instead of stenographic.
- That Dinner Tab Has Soared. Here Are All the Reasons. from the New York Times (with some awesome use of data visualization).
- 10 Ways to Lower Your Grocery Bill as Prices Increase from Healthline
- What the ‘historic’ Inflation Reduction Act means for your bank account from Fortune
January 18, 2024
The Journalist’s Resource has pulled together research on a hot topic: Why people think the economy is doing worse than it is. Take a look before the next jobs report comes out.
Reframing Headlines
November 11, 2021

This headline comes from KPIX, the CBS affiliate in the Bay Area, but it is far from the only time we’ve seen a story about homelessness center those who witness it rather than those who experience it. Framing a story in a way that positions threats to those in luxury condos as the primary impact of homelessness — rather than, say, the lack of safety and support felt by people who are actually experiencing homelessness — misses the point. If journalism seeks to help society deal with its collective problems, focusing on what support is needed by those without secure housing (and why they are not receiving it) is the right place to start.
For an example of what centering the narratives of those experiencing homelessness looks like, check out the San Francisco Chronicle’s “Homegrown and homeless in Oakland.” It privileges the stories of four local residents from a systemic, solutions-driven angle.
(I’ll also, as always, recommend Anita Varma’s research on covering homelessness in solidarity with those experiencing injustice.)
January 13, 2022


The first headline above is from a January 7, 2022 Associated Press story about a Labor Department jobs report. The second headline is from a Washington Post story — also published January 7 about the same exact report. Though both make accurate statements — unemployment did decline, and the economy did add 199,000 jobs — very subtle language choices give them very different framings.
AP chose to highlight lowering unemployment and “many more” people finding jobs. Both of those are widely regarded as good things, so this sounds like a positively framed story. The WaPo headline is decidedly more negative, all thanks to the word “just.” By using “just 199,000 jobs,” the reader is to understand that that number is not high enough. By what measure is unclear. Did experts predict a higher number? Does it vastly undercut current needs of the market? That question is almost unnecessary to answer because, such as you might lament, “there’s just one cookie left in the jar,” the message is clear: not good.
Though usually I use this space to mark a clear “do this, not that” conclusion, that’s less important to me here than the lesson the juxtaposition provides. The monthly jobs report is consistently reported on across major news outlets and often seen as a barometer of the economy. If two broadly trusted outlets can frame the same information so differently, it’s clear how turning to just one source for all of our news is fraught. Just like you should eat a variety of fruits and veggies, you should consume a variety of news. For even more comparisons on job reports headlines, check out media critic Dan Froomkin’s site Press Watchers.
April 28, 2022

The headline above, from ABC news, references the 2022 County Health Rankings report published by the University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute. From the story:
“The data reinforces what we’ve known for some time. People in both rural and urban communities face long-standing barriers, systemic barriers — avoidable barriers — that get in the way of groups of people and places in our country from being able to live long and well,” Sheri Johnson, co-director of County Health Rankings & Roadmaps and director of the University of Wisconsin Population Health Institute, told ABC News.
The acknowledgement of these systemic and avoidable barriers makes describing improved economic futures as “out of reach” an odd and fatalistic choice. The report does describe major inequality, but it does not, as far as ABC News reports, suggest it is mysteriously insurmountable or natural to U.S. life. Instead it clearly describes it as essentially man-made. The headline below, from United Press International, makes plain what the solution to this man-made problem of low, unequal wages is: pay increases! (From, one could infer, those creating the inequality.)

It’s crucial to understand how journalists play a role in establishing what is possible in the public discourse. This is a perfect example of two news outlets highlighting the same problem and framing the potential for that problem to be solved completely differently.
August 18, 2022
I have tried to ignore the discourse around “quiet quitting” (the act of doing what you’re paid to do, and nothing more; yes it’s poorly named) over the past few weeks. But I couldn’t escape articles by the Wall Street Journal, Fortune, Newsweek, ABC News, The New York Post, Refinery 29, HuffPost, Fast Company, Mic, and many more local and digital outlets.
I could write an essay on how the volume and trajectory of coverage of “quiet quitting” illustrates many problems of the news industry. (It followed the same path of so many other social media-mined stories: an explosion of shallow explainer articles titled with anxiety-inducing headlines, all soon to be forgotten. Is that time well spent? Do audiences walk away more informed?) Instead I’ll focus on the ways two headlines framed this “trend.”
I put “trend” in quotes because, while it is a social media “trend,” the spread of worker-focused resistance to capitalist burnout is no fad. In fact, that’s what many of those discussing the idea on TikTok are saying. The headline above from TODAY, however, likens it to any other social trend. Plus, by leaving the content of the discourse a mystery, it creates fear of the unknown. After all, “quitting” “taking over” during a strained labor market certainly sounds serious, especially to those who employ others.

The Independent does its readers a service in the headline above by not only describing the trending topic but by explaining its true nature. It’s about “acting your wage” and rejecting hustle culture, not actually quitting. Which, as many have found during the pandemic, is healthy! Framing such a mentality as mysterious or scary is disingenuous and de facto supports exploiting free labor.
August 25, 2022
I typically avoid using examples from Fox News in this space. That’s largely because I agree with media scholar Dan Froomkin that what the channel produces is not accurately described as news but is instead propaganda. It’s also because the juxtaposition such an example would create is often laughably transparent in its partisanship. Today I feel the comparison is worth making.
In August the Biden administration announced its long-awaited student debt plan. The Fox headline above makes no attempt to hide its opinion on the facts of the news. It refers to student loan forgiveness as a “handout,” a term long used to pejoratively describe public assistance. It also chooses to place the announcement against the backdrop of “as national debt soars. ” (This explainer from Quartz shows why the national debt is used as a scare tactic to avoid public spending, if you’re curious.) Fox could have easily chosen to end the headline with “as student debt soars” but that would paint the announcement in a positive light, which is not the goal here.
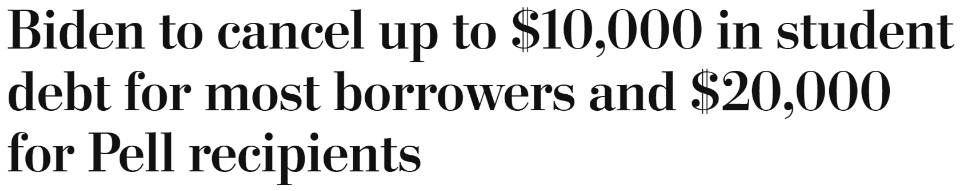
In contrast, the Washington Post’s headline tells it straight: what’s happening (loan cancellations) how it’s happening (who gets what money) and who’s doing it (Biden). No naked partisan slant to be found.
November 3, 2022
Before the U.S. Federal Reserve raised target interest rates in November 2022, CNN and CBS News both previewed the change online. The headline above was featured on CNN’s homepage the afternoon of the announcement. It gets the main point right, of course — the “hike” was historic. But it frames the event as “a problem for Biden,” presumably in that it would impact his approval ratings or his party’s election chances.
That may be true, of course, and considering November’s elections it may even be a relevant point to some. But, as research has shown, reporting that frames public issues as just fodder for the political game sows distrust among the public — in both the news and politicians.
CBS News’s take, below, not only piques the interest of the public by being service-oriented. It also reframes the Fed’s move as one that impacts people over politics. Yes, everything is political; but erasing voters from the conversation is just plain bad for civic engagement.
November 10, 2022
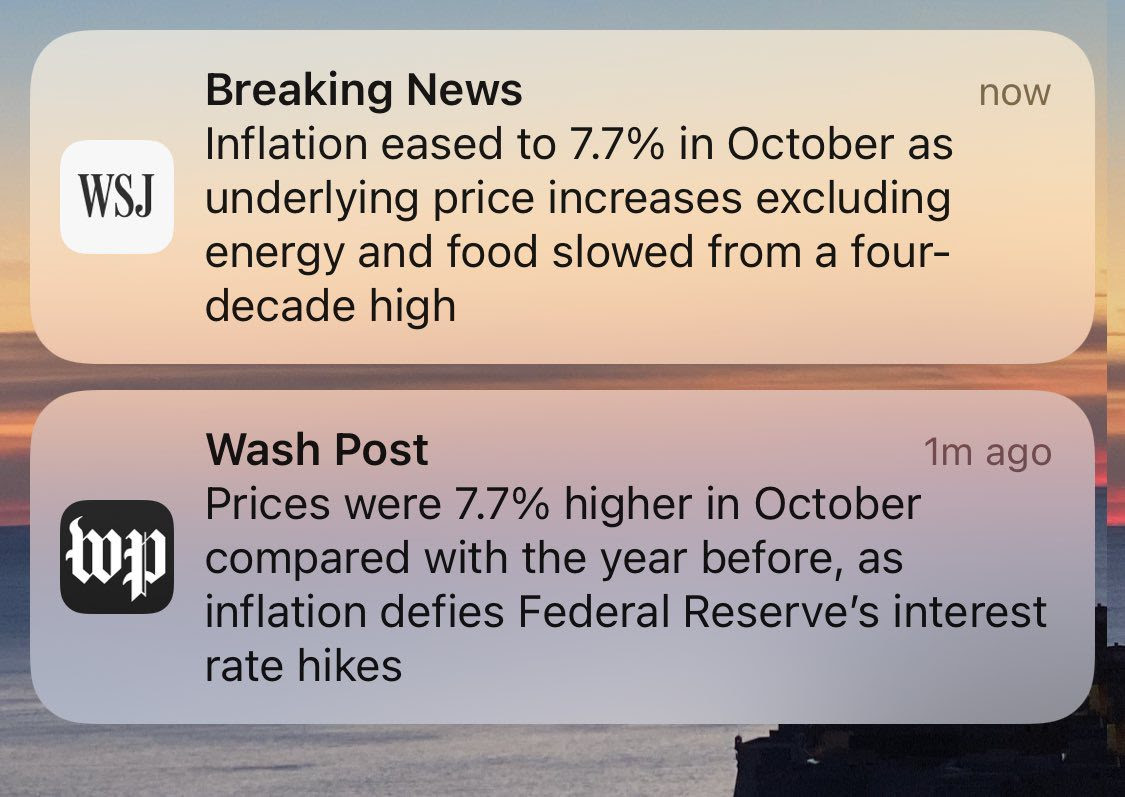
Shout out to Rachel Cohen of Vox for tweeting out this image of two similar push notifications from the Wall Street Journal and the Washington Post.
Just a few small words make these two framings different. The WSJ says inflation “eased to 7.7%,” putting the current rate in the context of larger trends. This context and the friendly word “eased” puts a rosier spin on the slowing of price increases. The Post, however, put that same number in the context of “defying” the Fed’s interest rate hikes, which were meant to slow inflation — you may remember this happened just a week before.
Which framing is “correct” may depend on your personal experience. Regardless, this juxtaposition shows how two mainstream media publications can frame the same news very differently in just a few words.
December 1, 2022
New York City Mayor Eric Adams recently announced a new initiative to address the visibility of homelessness in the city. Both the Washington Post and the New York Times reported on responses to the policy in the headlines below.

The Times’ headline above describes interviews with people experiencing homelessness who had varying reactions to the news. The focus on amplifying the voices of those who may be impacted by this news is certainly a positive.
However, it describes Adams’s initiative as “pushes to remove mentally ill.” The word “remove” is only helpful here if you’re looking to obscure what happens to the people in question once authorities deem them “removable.” People are not simply “removed” from a location without being placed elsewhere. This headline describes the situation like those experiencing mental illness and homelessness are not people at all, but are objects to be swept aside somehow.
The Post’s take, below, explains what removal really means in this scenario: forcible hospitalization. Explaining to audiences the consequences of such a policy — hospitalizing people against their will — is a key part of reactions to this news, and should be emphasized.
Unfortunately, both headlines exclude the word “people,” using the catch-all “mentally ill” to objectify and other a marginalized group. Such dehumanizing language is unacceptable in respectful, accurate coverage. Human-centered language — like “people with mental illness” or “people with mental health disorders” — is always preferred. Remember: longer, accurate headlines are better than catchier, dehumanizing ones.

December 15, 2022

The headline above is from the New York Times and describes changes that new owner Elon Musk has brought to Twitter recently. From this headline alone, the changes seem rather boring, business-as-usual stuff: budgets, legal teams and the like.
But if you read the deck or sub-headline which immediately follows, below, you’ll find some very unusual stuff. Twitter is just … not paying rent? And might not pay out severance packages? Excuse me?

For a business owner that isn’t as famous or rich as Musk, those decisions would likely be considered legal and ethical breaches. So it’s quite odd that the Times’ headline and its story refer to these as being done “to cut costs” and written up like your average brief. One can only wonder at how Musk’s power influences this framing of his decisions as normal business operations.
The headline from Insider below more appropriately puts the unusual aspect of this news front and center. (Though it does anthropomorphize Twitter in lieu of laying the action at Musk’s feet.)

March 2, 2023
Nearly three years ago, U.S. Congress enacted emergency legislation to provide economic assistance to the many people negatively impacted by the pandemic. This included raising the benefits available to recipients of the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program. In December, Congress signed into law a spending bill which directed this emergency SNAP distribution to end in March, though federal public health emergency declarations won’t end until May. Research shows the emergency allotments kept 4.2 million people out of poverty in the fourth quarter of 2021, reduced poverty by 9.6% in participating states and similarly reduced child poverty by 14%. An estimated 30 million U.S. residents are expected to have their SNAP benefits cut.
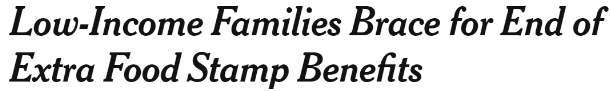
The headline above, from the New York Times, rubs me the wrong way for a few reasons. For starters, it uses “food stamp benefits,” which the government moved away from in 2008 due to stigma, instead of SNAP. Research has repeatedly shown that Americans support “assistance to the poor” much more than they specifically support “welfare,” another stigmatized term. I imagine historic baggage might make “food stamps” function similarly, hence the renaming. Public programs unfortunately often require some linguistic gymnastics (also called the euphemism treadmill) to remove their stigma.
This headline also simply uses the word “end” to describe what’s happening to these benefits. Without ascribing a cause, “end” makes it sound like a natural demise, not the result of choices made by humans. Also, simply referring to those affected as “low-income families” doesn’t give the audience an understanding of the scope of the problem. Finally, there’s the use of “extra,” which by one definition means “additional” but by another means “excessive” or “extravagant.” Money that keeps people from starving is certainly no extravagance. I would’ve chosen a different word.

I much prefer the headline from Kaiser Health News, above. It accurately names SNAP and describes them as “emergency” benefits, not “extra,” which underlines the reason for the initial expansion. It also names the impact of this change in an easy-to-digest way in that it will “threaten food security” for a huge swath of the public. It’s incredibly important audiences understand the domino effect this change will have on their communities.
Finally, this headline uses “cuts” to describe why these benefits are disappearing. “Cuts” implies action and intention. It implies someone (in this case, Congress) had the option not to cut these benefits, but chose to instead. It’s crucial that we link harms like food insecurity to their causes: decision-makers. Remember, we know these benefits kept millions out of poverty. Poverty is a policy choice.
April 13, 2023
What do each of the headlines below (from the Wall Street Journal, Fortune, WTOL11, and Axios, respectively) have in common? Each accepts the premise of the U.S. “worker shortage.” You may have heard that businesses are having a hard time finding workers. You may have even heard that “no one wants to work anymore.”
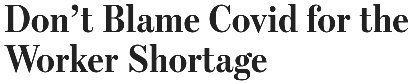



According to the facts we have available, however, that just isn’t true. Recent Labor Department data says nearly 81 percent of workers ages 25 to 54 are employed, the highest share of these “prime-age workers” employed since 2001. So what’s happening?
Well, we live in a capitalist society, where supply and demand rule. A true shortage could be spurred by workers demanding wages that are too high to support business. But we don’t have that problem. “Wages in the U.S. have stagnated since the early 1970s,” CNBC reported last year. Meanwhile, in 2022 U.S. corporate profit margins reached their widest since 1950, “suggesting that the prices charged by businesses are outpacing their increased costs for production and labor,” Bloomberg reported.
The great podcast Citations Needed just released an episode on this topic that’s well worth a listen. The hosts say of the mythical shortage (emphasis mine):
“It creates an inciting incident that sort of justifies these horrible right-wing policies….Basically, the labor shortage as a sort of trope is a skeleton key for whatever horrible anti-worker thing one wishes to jam down people’s throats.”
So how could these headlines improve? For starters, they could stop referring to a “worker shortage” to begin with and explain labor dynamics to their audiences. It’s the news media’s job to deconstruct false narratives like these (that we help create!) so our communities can make informed decisions about their lives. For instance, should the specter of a labor shortage really be used to weaken protections for child labor while violations are on the rise? Several state legislatures think so, apparently.




Instead, we should amplify the heart of the matter: a system of worker exploitation. The headlines above do just that. They’re from local outlets Fox5, ABC7, and WXII12 — and the final example isn’t even from a news outlet! It’s from the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, and it includes surveys and interviews with workers on what they’re looking for. It’s frankly the best human-centered reporting I saw in my search for today’s newsletter. Go figure.
September 21, 2023
Recently, I referred to my own focus on the subtleties of news language as sometimes “splitting hairs” and my colleague Gene Sonn generously corrected me. “It’s not splitting hairs, it’s being precise,” he said.
This was on my mind this morning as I encountered the CNBC headline about the United Auto Workers strike below.

The word “because” here made my ears perk up. General Motors and Stellantis are two of the three automakers workers are striking against, so their public statements have emphasized these layoffs as a consequence of those strikes. The strikes are disrupting production lines as intended, which has downstream consequences. In that way, “because” is shorthand for this domino effect.
It’s just one word, but “because” here also subtly assigns complete fault to the strike. However, the strike isn’t happening in a vacuum; it is a response to the wages paid by the automakers. As has been widely reported, the CEOs of Ford, Stellantis, and GM make 281, 365, and 362 times more than their average workers, respectively.
The automakers could choose not to layoff workers during this strike, or end it by compromising with UAW. They have options and they have agency here, regardless of anyone’s opinion of which choices they should make. It’s important that journalists communicate that agency with the nuanced language at their disposal.
To put a finer point on it, an accurate headline could just as easily read, “GM and Stellantis laid off 2,000 workers instead of agreeing to UAW demands” or “GM and Stellantis lay off workers instead of cutting CEO pay.”
Or, like Axios did below, a headline could use the phrase “amid ongoing UAW strike,” which doesn’t note any cause of the layoffs. It merely draws a temporal connection for the reader.

September 28, 2023
I tip my hat to writer Joshua P. Hill for the viral tweet that alerted me to this story.
As the old journalism adage goes, “If your mother says she loves you, check it out.” Fact-checking and corroborating a source’s story are crucial steps in the reporting process.
Yet, all too often, rehashes of public statements are published as complete news stories. The most generous justification for this habit is that what is considered “newsworthy” in these cases is not whether a statement is true, but that the statement was made, or that it was made by an important entity. In that case, the public deserves to know what that entity has said as soon as possible.
The obvious problem here is that if journalists make the argument that anything said by a certain entity is inherently newsworthy, then they are absolved of the need to actually determine whether their claims are true before amplifying them. A statement might not be true, but the fact that the Very Important Person said it is true, so we’re in the clear, so to speak.
That’s how we get headlines like the one from CBS below. Target recently announced that they will close nine of their over 1,900 U.S. stores. Their public statement included the words, “we cannot continue operating these stores because theft and organized retail crime….” Instead of using quotation marks or attribution to couch this statement, this headline uses “because,” which makes Target’s claim read like objective fact.

But it’s not objective fact. It’s a statement made by a large corporation that could be true or false.
Why does the veracity of Target’s claim matter? For the past few years, headlines about rising retail theft have proliferated — including regurgitated corporate statements like these. This coverage has increased public perception that this is a rising threat. This has led lawmakers from California to Pennsylvania to bolster law enforcement and consider legislation that would worsen punishments for perpetrators. In other words, similar claims have impacted public life by shifting resources and laws. We should know whether they’re true — and, as is journalistic best practice, we should not take one source’s word for it.
What other information should be considered alongside Target’s claim? For starters, the latest National Retail Security Survey “found the effect of theft on retailers’ bottom lines is about the same as it has been for years,” CNBC reports. Other research on the topic shows claims of a retail theft crisis are murky at best. CNBC also reports that “Target’s business has struggled for more than a year with company-specific challenges, including a glut of unsold inventory, backlash to its Pride merchandise collection and a pullback in consumer spending.”
It may be impossible to determine the objective truth here — maybe Target has a decision-making paper trail to uncover, or maybe it doesn’t. But that doesn’t mean its corporate statements should be taken at face value and amplified.
The headline from the Washington Post below does a good job of balancing this. The fact is that stores are closing. The reason for doing so is unverified, so it reads that Target “blames” it on theft, leaving the truth up for debate.

October 5, 2023
Over 75,000 workers for the Kaiser Permanente health care system began a three-day strike during the first week of October. CBS News reports that it’s the “the largest walkout by health care workers in U.S. history,” and “curtailing nonessential care like routine checkups” for millions.
The New York Times headline below is, of course, technically accurate. But it’s so slim on the details that it’s almost boring. The one “plus” I’ll give it is that it doesn’t assume readers know that Kaiser Permanente is a health care company.

When I read the headline below from CBS News I thought, “That’s more like it.”
For starters, it names the historic nature of this particular strike at the jump. With all the labor headlines in the news this summer, it’s important that audiences get a sprinkle of context where they can.
Speaking of context, this headline also includes some incredibly important information that the NYT does not: why the workers are striking! Of course, it’s a given that workers going on strike are seeking better conditions. But when such a strike will disrupt operations for many folks outside of its industry, it’s crucial they understand what it’s for. And in this case, it’s likely something everyone can agree on: understaffing in the health care system is no good.

November 2, 2023
As the saying goes, “those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it.” Sadly, this rings true for journalists who haven’t learned the lessons of prior coverage and its criticisms.
Back in 2005, in the wake of Hurricane Katrina, two wire service photos of the resulting crisis sparked a conversation on language and framing. The Los Angeles Times recounted the story in 2017:
“One from Associated Press photographer Dave Martin showed a young black man wading through water while holding a bag and a case of soda. The accompanying description stated that he was ‘looting.’ A second photo from Chris Graythen for Getty Images showed a similar scene, but this time it was a white couple clutching bags of food. Their actions were labeled as ‘finding.’”
The difference in these terms is the level of sympathy elicited for the subject. “Looting“ implies criminality while “finding” in this context implies innocently gathering goods for survival. Based on U.S. history, I think I can reasonably suggest systemic racism played a role in the labels given to each photo.
I use this example pretty frequently in my workshops on news and language. You may understand, then, why the headline from Politico below caused me dismay.

The humanitarian crisis in Gaza is well documented. More than 8,000 Palestinians have been killed in the past few weeks and innocent civilians are in dire need of aid. Using the word “loot,” traditionally defined as pillaging for the spoils of war, is an incredibly cynical and unsympathetic way to frame people stealing for survival.
I much prefer the simple rephrase used by CNN in the headline below. “Take” is a pretty neutral verb in this situation; it doesn’t imply criminality but does suggest the goods weren’t willingly given. The use of “basics” underlines the life-sustaining nature of the items people were searching for.

The final example below, from the BBC, I think does the best job of illustrating how dire the situation truly is. It uses the phrase “break into” to imply that the actions described may not have been lawful, but still manages to focus on the real story here: people are desperately searching for aid. This isn’t stealing for stealing’s sake — as we might think of with the word “looting.”
This headline doesn’t sensationalize the events it describes by centering crime. Its priorities are clear: audiences need to understand how bad things really are. It’s the difference between, “Look, these people committed a crime” and “Look, things are so bad these people had to commit a crime to survive.”

Critical Voices
Couldn’t agree more with writer Zito Madu here. Language is a powerful thing and so much of communication requires using comparisons to help others pick up what you’re putting down. This social media presentation uses a metaphor to describe workers making the choices that feel right for them like a disease, a frame so negative and pro-capitalist it’s hard to overcome, regardless of the article’s contents.
Re: an earlier Headline Check, The Hill reporter Zack Budryk gets to the heart of what reporting on this “trend” is all about.

There’s not much one can add to comedian Jacob Hatton’s exclamation at this recent Telegraph headline. If landlords are facing a crisis, what do we think the renters are going through?

Civil rights lawyer Alec Karakatsanis (a favorite follow of mine) brings up a great point. Wells Fargo will be paying $3.7 billion to settle charges that it wrongfully seized homes and cars from customers, among other harms it committed against “millions of American families,” according to the director of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. The way enormous wrongdoing by large financial institutions is reported on is far different from, say, the dramatic coverage of shoplifting we’ve seen over the past year. It’s worth contemplating why white collar crime that affects millions receives a less sensational tone than petty crime.

Yes, this is a real Wall Street Journal headline. There’s not much more to say that Alan MacLeod of Mint Press News hasn’t already said. The framing of this story about inflation and egg prices is giving “let them eat cake” vibes.
“We are living through the end of the useful internet. The future is informed discussion behind locked doors, in Discords and private fora, with the public-facing web increasingly filled with detritus generated by LLMs, bearing only a stylistic resemblance to useful information. Finding unbiased and independent product reviews, expert tech support, and all manner of helpful advice will now resemble the process by which one now searches for illegal sports streams or pirated journal articles. The decades of real human conversation hosted at places like Reddit will prove useful training material for the mindless bots and deceptive marketers that replace it.”
— Alex Pareene, “The Last Page of the Internet,” Defector
Pareene wrote this in response to the profit-focused changes coming to Reddit, the punchline-turned-
Writer, vlogger, and head of educational video company Complexly Hank Green wrote this in reference to his brother John’s recent video about a controversial Johnson & Johnson patent extension. (Full disclosure: I once did freelance work for Complexly and, though I never interacted with Hank, I do think he’s super smart.) But I find his point broadly applicable to any writing about corporations and their decision-making. News media plays a large role in framing the movements of impactful corporations as autonomous, as if there aren’t humans making choices behind the curtain. We should be careful to explain to audiences who is pulling the strings.

MSNBC host Mehdi Hasan tweeted the above in response to a Wall Street Journal poll showing that many Americans mistakenly think the economy and inflation have gotten worse over the past year. The first part of his quote has certainly been said before; journalists must always consider their role as educators of the public. But the second part — not deferring to those poll results as “reality” — is what’s most important here. If public opinion does not align with the facts, we should not let those feelings dictate our framing of the facts.

Sam Bankman-Fried founded the cryptocurrency exchange FTX and his fraud trial was in the news in early October. Journalist Jacob Silverman’s tweet is a timely reminder, likely made in response to headlines that frame him as a “wonder child,” “boy genius,” and “math nerd.”

Cosmologist Katie Mack’s poignant take on the latest study on basic income makes me wonder how many basic income experiments must see positive results (Stanford has a global map of them!) before the concept is framed as anything but a fringe idea in the press. How would the media treat the repeated trial of a life-saving medication without any real-world implementation?
“Whether the social ill is the hungry or the unhoused, responsibilization puts the onus on the individual. ‘Consumers,’ the study continued, ‘are now expected to address a wide variety of social issues through their individual consumption choices (e.g., global warming, income inequality) whereas in the past these issues would have been addressed structurally by governments, as part of a broader movement of individualization.’”
— Devin Thomas O’Shea, The Story of Late Capitalism as Told Through Panera Bread
This excerpt quotes a 2018 study published in the Journal of Business Ethics. The study, combined with O’Shea’s spirited retelling of the legacy of Panera Bread, has brought this word “responsibilization” into my vocabulary. It really encapsulates many ways capitalism has reframed systemic issues as individual ones, and how media often follows suit. You’ll certainly see that word here again.

That sound you hear in the distance is my eternal groan, which has been echoing across the land since I read this very real New York Times headline.
The fact that whoever wrote this headline (tweeted here by The Lever founder David Sirota) believes this is an acceptable position for the Times to take — and it is a position, to suggest public safety and private profit must strike a “balance” and not be clearly tilted towards the public good — troubles me deeply. It’s especially troubling following report after report of Boeing’s quality control issues following a January 5 incident that put passengers in danger.

Vulture TV critic Roxana Hadadi’s comment on a recent radio report she heard should provide perspective for anyone reporting on the economy. At what point is “grocery-specific inflation” the wrong term for price gouging? How can news media frame this issue so that audiences understand who and what is controlling grocery prices?
Must-Reads
Tired, Filthy, and Overworked: Inside Amazon’s Holiday Rush
Anna Kramer, Wired
In need of a last-minute gift? Wired’s look into what really happens when you choose expedited shipping — to the exhausted people working through pain to put those items into cardboard boxes — will have you thinking twice.
How Not to Cover a Bank Run
Brian Stelter, The Atlantic
The coverage of the Silicon Valley Bank collapse has been a whirlwind. Media critic Brian Stelter writes for the Atlantic about how financial reporters have dealt with previous bank runs and the difficult decisions they have to make. His take underlines the very chicken-and-egg nature of the news media’s impact on the world around us.
How a Big Pharma Company Stalled a Potentially Lifesaving Vaccine in Pursuit of Bigger Profits
Anna Maria Barry-Jester, ProPublica
ProPublica is known for its powerful, corruption-exposing investigations, and this is no different. The story of how pharmaceutical giant GSK put profits head of saving lives with its tuberculosis vaccine is the stuff of cartoon villains. But it’s worth a read to understand just what systems are at play in global health care.



